Quantitation: Competition Assays
Competition assays are suitable for the detection of small molecules. In this detection approach, the AuNPs-functionalized sensing surface is modified with target analytes. During a sensing event, a sample containing free-flowing analytes is premixed with corresponding bio-receptors and subsequently introduced to the sensing surface. The free-flowing analytes and the bound analytes then engage in a competitive interaction for binding to the bioreceptor. The binding of bio-receptor to the bound analyte results in an optical response, which can then be used to detect and estimate the concentration of the target analyte in the sample.
定量:競爭檢測法
競爭檢測法適用於小分子的檢測。在這種檢測方式中,帶有金奈米粒子(AuNPs)的感測表面會先與目標分析物進行修飾。檢測時,包含游離分析物的樣品會先與對應的受器混合,然後再引入至感測表面。游離分析物和固定分析物會彼此「競爭」與受器結合,而受體與固定分析物的結合會產生光學反應,可進而偵測並推算樣品中待測物的濃度。
Target: methamphetamine (MA) in urine
Methamphetamine (MA) is a highly addictive stimulant drug. The abuse of this illicit drug can lead to harmful effects on the central nervous system, extreme weight loss, severe dental problems, organ failure, or death.
目標:尿液中的甲基苯丙胺(MA)
甲基安非他命(MA)是一種高度成癮的興奮劑,濫用這種非法藥物可導致中樞神經系統的危害、體重極度下降、嚴重的口腔問題、器官衰竭或死亡。
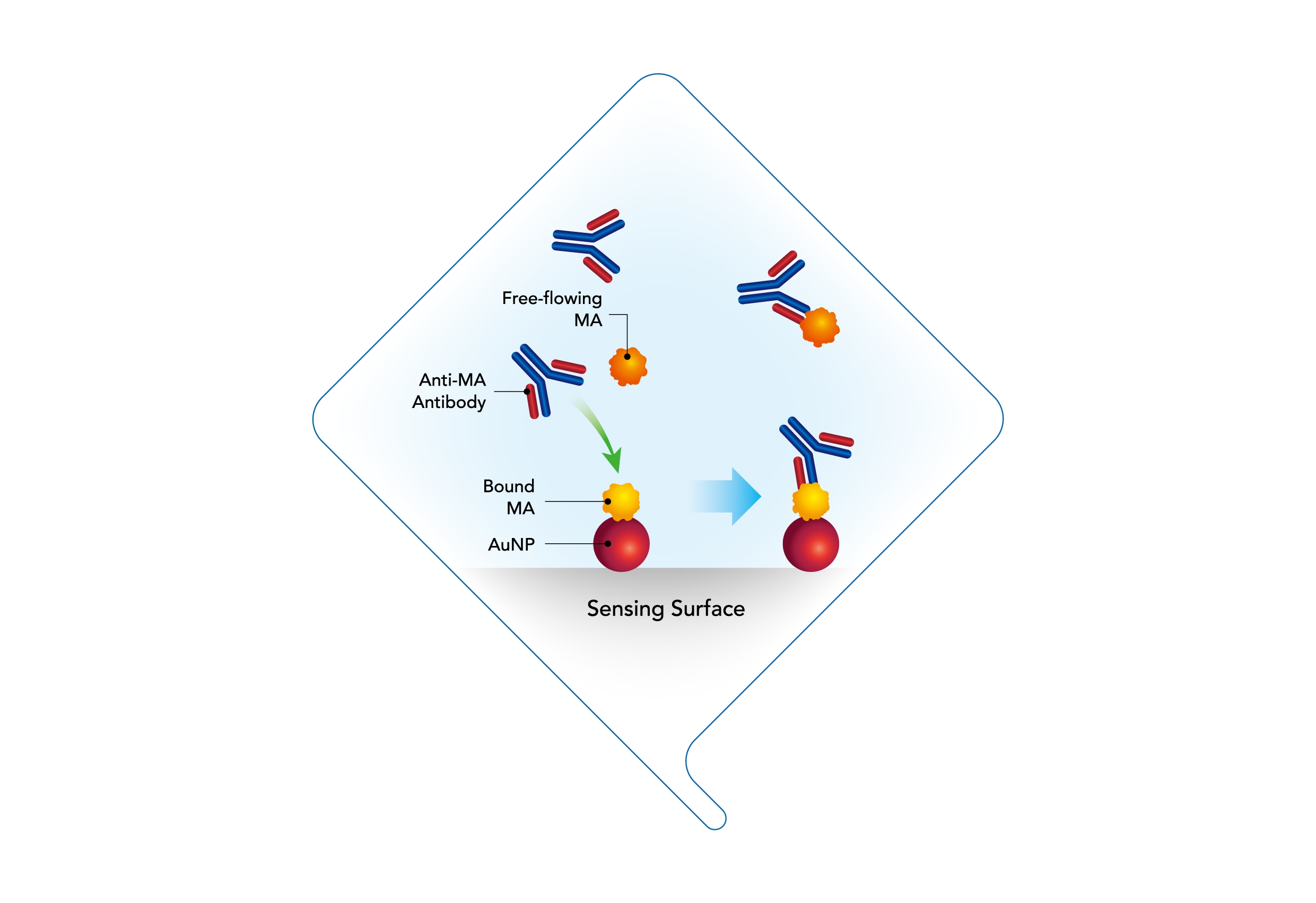
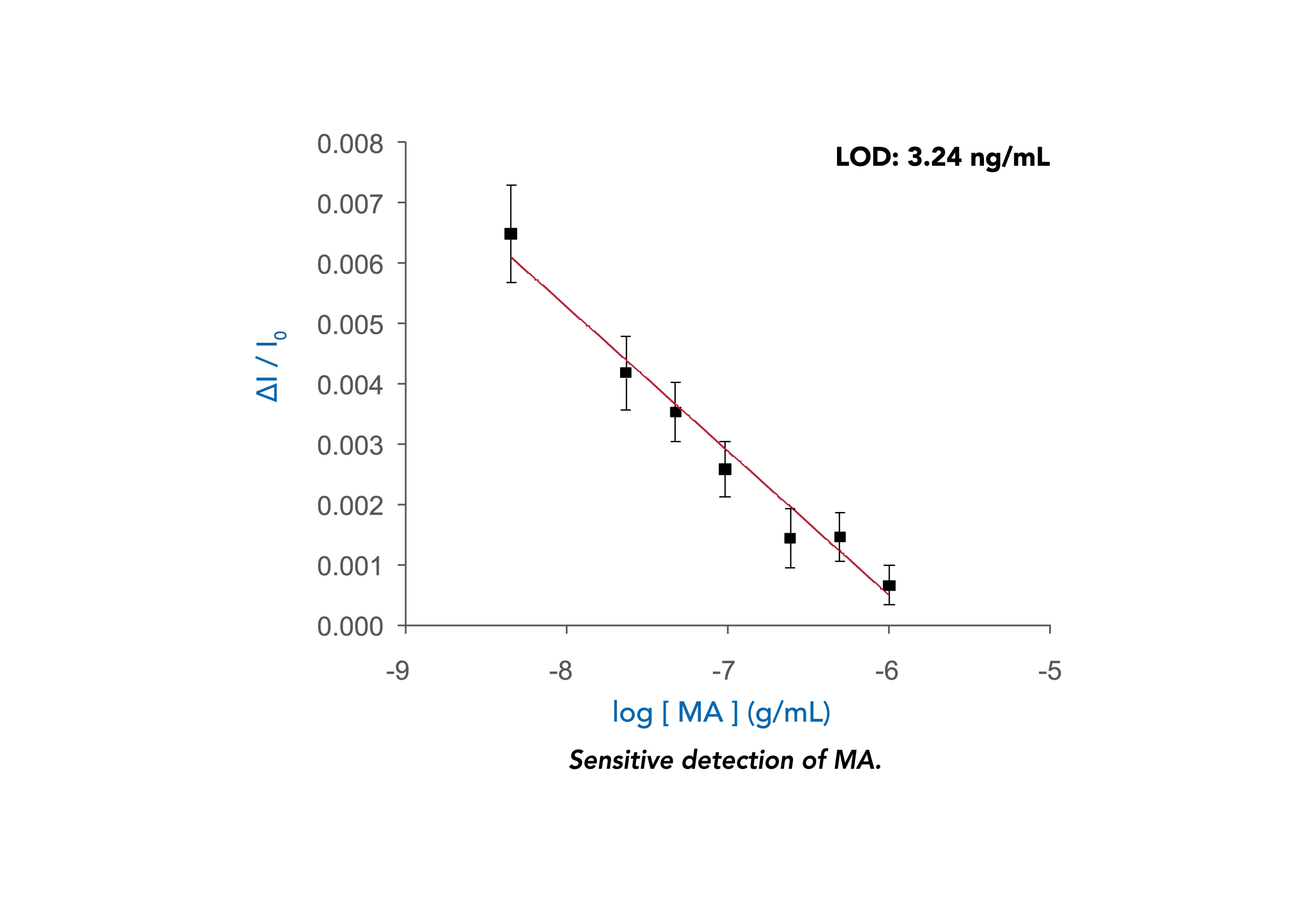
A known concentration of MA is first functionalized onto the sensing surface. A sample of free-flowing MA with unknown concentration premixed with anti-MA antibodies is then introduced to the sensing surface. Bound MA and free-flowing MA “compete” for the anti-MA antibodies during detection. Binding of anti-MA antibodies to the bound MA results in a refractive index change at the sensing surface and produces an optical response.
首先將已知濃度的甲基安非他命(MA)固定到感測表面上,然後將含有未知濃度的游離MA的樣本與抗MA抗體預先混合,並引入到感測表面。在檢測過程中,固定的MA和游離的MA將競爭著與抗MA抗體結合,抗MA抗體與固定的MA結合後會導致感測表面的折射率變化,產生光學反應。